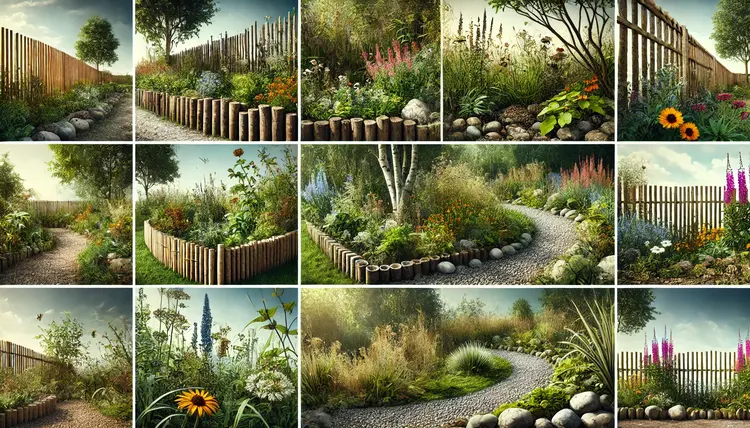
Rain Garden Designs: Eco-Friendly & Attractive Landscaping Ideas
Published: 14 Apr 2025
Introduction to Rain Gardens
A rain garden operates as a designed landscape structure which captures and incorporates rainfall that drains from roofing materials and pavement areas. Such garden installations contribute to both flood prevention and maintain soil stability while bettering water resources. A design using native plants along with porous soil lets rain gardens cleanse pollutants immediately before the water enters the soil instead of going to storm drains.
Rain gardens serve both functional and aesthetic purposes by enhancing outdoor appearance besides their utility aspects. These gardens sustain a rich habitat for butterflies and bees while being a practical water management solution because they shelter numerous birds.
Benefits of Rain Gardens
Rain Garden Designs installed in your yard comes with various environmental advantages along with attractive features.
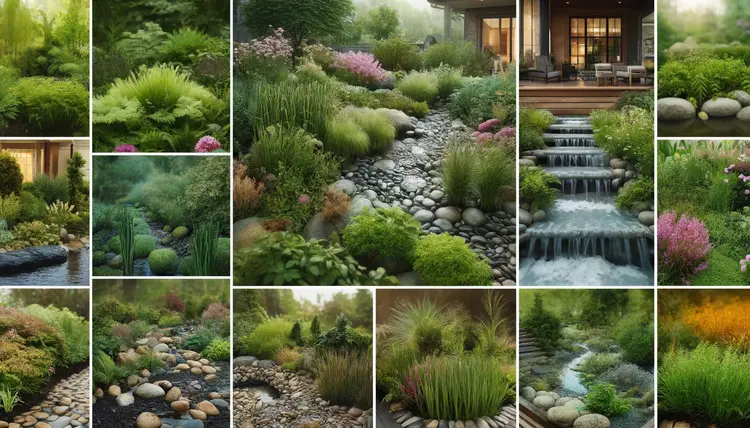

Key Benefits
- Water Filtration: These gardens function as water filters to prevent the buildup of water in lower regions.
- Soil Stability: Soil stability occurs because rain gardens are strategically located, which minimizes slope erosion.
- Pollution Control: Native plants in garden areas function as polluters of water runoff by capturing and biologically degrading pollutants.
- Groundwater Recharge: Water from rain drains down into the groundwater reservoir instead of running straight into drainage channels.
- Wildlife Habitat: Rain gardens serve as wildlife habitats by creating suitable habitats and food sources which support pollinators together with helpful insects.
- Aesthetic Appeal: Rain gardens improve landscape aesthetics through their use of colorful flowers combined with flourishing greenery which enhances neighborhood appearance.
Design Element | Description | Benefits |
Native Plants | Use drought-tolerant, water-loving native plants. | Reduces water usage, supports local wildlife. |
Permeable Soil | Incorporate well-draining soil to help water absorption. | Prevents water runoff, promotes groundwater recharge. |
Rainwater Harvesting | Add a rain barrel or cistern to capture rainwater. | Reduces water bills, conserves water for dry spells. |
Boulders & Rocks | Strategically place rocks and boulders for natural filtration. | Adds visual appeal, prevents soil erosion. |
How to Select the Optimal Site for a Rain Garden
The initial step towards constructing a rain garden starts with selecting its optimal placement.
Site Selection Considerations
Before designing rain gardens, one needs to select an optimal site that will function and look attractive.
- Distance from Buildings: The garden should sit at least 10 feet away from buildings to avoid water-induced foundation problems.
- Natural Drainage Areas: The rain garden placement must occur at sites where water naturally drains such as by foundations and downspouts.
- Soil Type: Select sites located away from soil surfaces which are tightly packed or resist water drainage. A percolation test on the soil should be performed to verify correct water absorption rates.
- Sunlight Exposure: Sunlight exposure needs to be between full sun and partial shade according to the selected plants.
- Positioning: The position of the garden needs proper planning to deliver efficient functions while supporting the landscape design.
Establishing a Rain Garden That Functions Properly
An effective rain garden balances aesthetics with functionality. Consider these essential design elements:
1. Garden Shape and Depth
- Choose a form that suits the natural appearance of the area.
- Dig a collection zone with a depth ranging from 6 to 12 inches deep for the absorption of water.
2. Soil Preparation
- A mixture of sand, compost and topsoil will enhance your ground drainage.
- Soils that become compacted impede the process of wet water seeping down into the ground.
3. Plant Selection
- Utilize plants that thrive under wet and dry situations in your area.
- Multiple species of grasses, shrubs and flowers should be selected to achieve biodiversity across the system.
4. Mulching and Edging
- A layer of mulching material should be used to stop weed growth and maintain water levels.
- The garden edges should be defined by applying decorative stones, logs
- or bricks.
Rain garden efficiency combines with visual appeal when appropriate design principles are followed.

Best Plants for Rain Gardens
The success of a rain garden heavily relies on making suitable plant choices. Different plant species must be selected according to their capability to grow under diverse water conditions.
Native Flowers and Perennials
- Black-eyed Susan produces yellow blooms which also serve as a pollinator magnet.
- Purple Coneflower demonstrates both durable plant characteristics along with drought resistance once it takes root.
- Swamp Milkweed – A great plant for butterflies and wet conditions.
Grasses and Ground Covers
- Native grasses referred to as switchgrass adapt to both dry and wet soil environments.
- The light-leafed Blue Sedge brings smooth flowing textures to edge areas of your garden.
- Creeping Jenny demonstrates excellent spreading behavior which additionally helps to stop soil from eroding away.
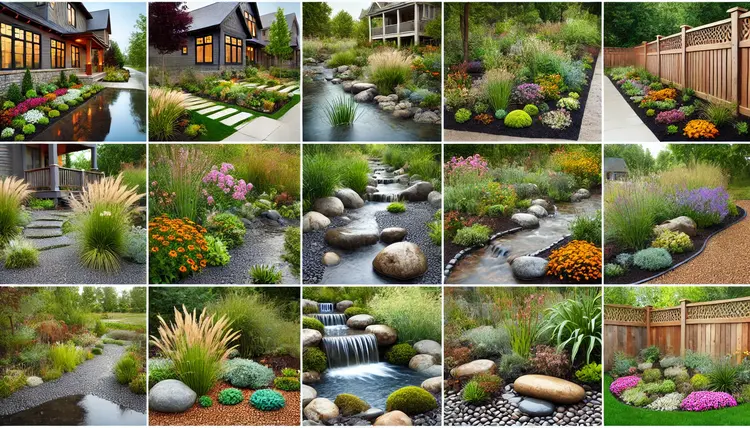

Shrubs and Small Trees
- Red Twig Dogwood – Offers striking red stems in winter.
- Buttonbush – A pollinator favorite with unique spherical flowers.
- Winterberry Holly – Produces beautiful red berries that make an attractive addition to any season.
A combination of the selected plants leads to an eco-friendly rain garden that grows successfully.
Creative Landscaping Ideas for Rain Gardens
Artistic features should be used to make rain gardens more attractive.
- Add sizable decorative stones as rock features to generate visual texture together with climactic distinction.
- A walking path through the garden should be installed as both an access feature and an aesthetic enhancement.
- The garden should follow curving lines instead of straight alignment to create natural beauty.
- Tall vegetation should be positioned in the center, followed by shorter plant varieties which should be placed at the garden edges.
- Building a plant variety that includes flowers appearing at different times throughout the year helps create continuous garden beauty.
The purpose of rain gardens should be functional design along with serving as attractive landscape features.
Design Element | Description | Benefits |
Water-absorbing Pathways | Install pathways that allow rainwater to percolate into the soil. | Helps water flow into garden, reduces runoff. |
Mulching | Add a layer of mulch to retain moisture and improve plant health. | Conserves moisture, improves plant growth. |
Overflow Drain | Ensure the garden has an overflow drain to manage heavy rainfalls. | Prevents flooding and ensures proper drainage. |
Rain Garden Borders | Use attractive borders like stones or shrubs to define the garden. | Enhances the aesthetic appeal and structure of the garden. |
Maintenance Tips for a Healthy Rain Garden
Regular care allows both the proper operation and visual appeal of the rain garden to remain intact.
Key Maintenance Steps
- Weed Control measures should remove all invasive weeds since they compete with native plants for resources.
- Each year replace mulch because this practice helps retain moisture while inhibiting weed growth.
- Check the soil condition through inspections to monitor any signs of erosion or compaction then provide adjustments as needed.
- Citizens should perform plant trimming by cutting dead foliage in late winter to promote new plant growth.
- Plant watering should continue during dry conditions until the new root system maintains itself.
Normal maintenance requires only a few steps for a rain garden to keep its flowers alive while becoming an attractive landscape element.

FAQs
What purpose does a rain garden serve?
The purpose of a rain garden includes capturing excess stormwater that prevents flooding and filters out pollutants simultaneously.
How long does it take to construct a rain garden?
The total time needed to construct a rain garden depends on multiple factors. Proper planning and available materials allow the installation of most rain gardens during a typical weekend.
Do rain gardens attract mosquitoes?
An appropriately designed rain garden will drain its water within two days, thus obstructing mosquito development.
Can rain gardens be built in clay soil?
Yes, as a solution, soil needs amendments including both sand and compost to receive proper drainage.
How do I know if the rain garden functions appropriately?
The rainwater drainage should occur in not more than two days, while plants need to stay healthy in dry conditions.

Conclusion
The implementation of a rain garden serves two essential purposes: it functions as a water management system and simultaneously adds visual appeal to outdoor spaces. Propelling from the right site selection along with practical design choices and suitable plant selection enables homeowners to generate an efficient landscape masterpiece. Rain gardens require minimal care to achieve both short-term environmental advantages and they convert simple landscapes into vibrant natural habitats.
Implementing a rain garden in your property establishes dual benefits through sustainability contributions and establishment of attractive and robust exterior spaces. Initiate your rain garden project now to experience its functional aesthetics and add them to your household.

- Be Respectful
- Stay Relevant
- Stay Positive
- True Feedback
- Encourage Discussion
- Avoid Spamming
- No Fake News
- Don't Copy-Paste
- No Personal Attacks

- Be Respectful
- Stay Relevant
- Stay Positive
- True Feedback
- Encourage Discussion
- Avoid Spamming
- No Fake News
- Don't Copy-Paste
- No Personal Attacks